Project Overview
An offshore gas injector well operated by ADNOC Offshore was experiencing sustained pressure buildup in both its A and B annuli, creating the need for a reliable, full-wellbore diagnostic solution. The well’s complex dual-completion design, high H₂S levels (~7%), and multiple potential cross-flow paths made it difficult to identify the source of the problem using conventional methods. Without accurate and timely insight, the pressure behavior posed increasing operational and integrity risks.
Conventional intervention methods were limited by platform access, personnel constraints, and the requirement to log each annulus separately. To obtain full-wellbore visibility in a single operation, the operator deployed a single-use Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) system capable of capturing continuous DAS/DTS data during one rigless run.
The solution incorporated interrogator technology from AP Sensing, enabling high-resolution Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS)
and Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS)
across the well.
By leveraging this capability, the operator achieved complete annulus coverage, reduced investigation time and evaluated DFOS performance under real field conditions, especially its ability to detect low-rate, transient leak events.
Solution
To investigate the pressure anomalies, the operator deployed a single-use, dynamically de-spooled DFOS probe from WellSense, allowing bare fiber to free-fall into the well without wireline or slickline. The probe carried several thousand meters of optical fiber and was launched through a compact launcher above the well, with a secondary fiber link connecting the wellhead to the DAS and DTS interrogators.
The interrogator units used in this deployment were supplied by AP Sensing, whose advanced DAS N52 Series
and DTS N45 Series
technology formed the backbone of the monitoring system.
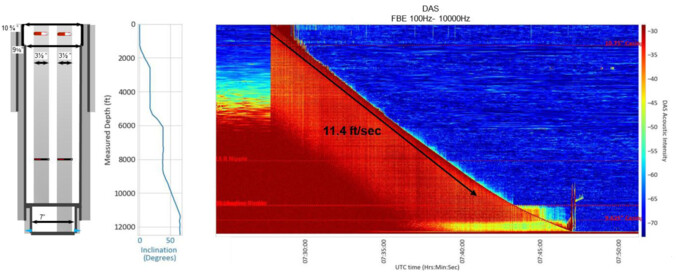
DAS and DTS together provided a clear leak-detection workflow. DAS identified acoustic signals from escaping fluids, pinpointing and characterizing leak activity. DTS detected temperature changes caused by fluid movement, revealing leak depth and distinguishing whether the well was taking fluid in or leaking out. The probe reached roughly 3,700 m in about 20 minutes, delivering continuous DAS and DTS coverage across the entire well. Once positioned, the fiber remained stationary while DTS recorded temperature anomalies and DAS captured high-frequency acoustic signals and highly sensitive low-frequency (LF) responses (<0.5 Hz), crucial for detecting subtle, low-rate leak behavior.
A structured sequence of bleed-downs and controlled injections was then performed to stimulate potential leak paths. The full diagnostic program was completed in a single pass with minimal footprint and reduced personnel.
Results & Benefits
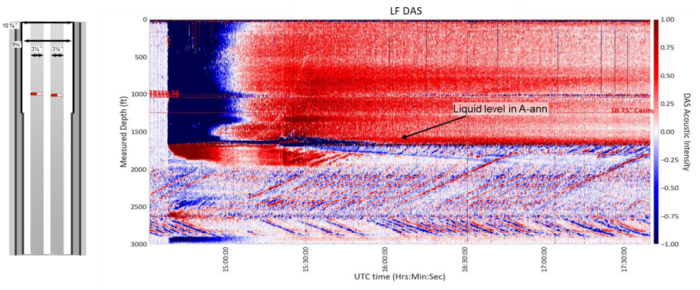
The DFOS survey clearly identified the inner tubing as the main leak source and revealed multiple communication points with the annulus. Acoustic and temperature anomalies indicated gas ingress, while LF-DAS captured slow strain changes and complex flow patterns, showing both upward and downward movement during pressure manipulation.
The high-resolution data provided by AP Sensing’s interrogators enabled accurate identification of the fluid level and gas–liquid interface, delivering a complete view of the wellbore’s behavior in a single run. The diagnosis was completed in under 14 hours, far faster than conventional multi-run logging. This reduced deferred production avoided a separate leakratesurvey and minimized emissions and personnel exposure. The integrated dataset delivered highconfidence inputs for ADNOC’s risk-ranking workflow.
Conclusion
This project showed how rigless DFOS deployment combined with AP Sensing’s DAS and DTS technology delivered full-wellbore visibility in a single operation. The approach enabled rapid leak detection, reduced investigation time, and provided reliable data for riskbased decision making.
The content of this case study is based on this paper in the OnePetro online library : SPE-228898-MS