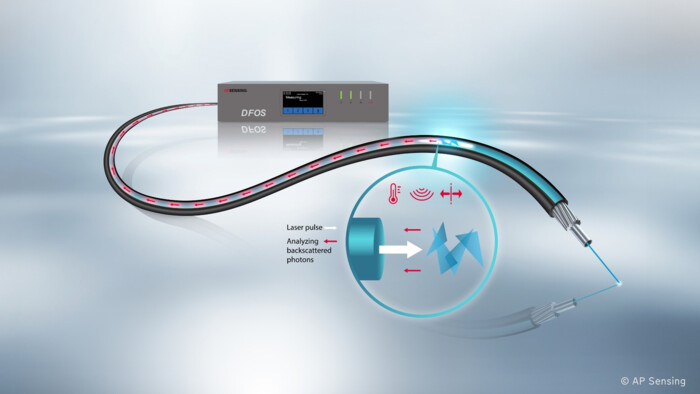
Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) systems provide critical asset monitoring by utilizing standard fiber optic cables as sensors. These systems enable precise measurement of temperature, strain, and acoustic signals along the entire length of an optical fiber. DFOS technology plays a crucial role for the monitoring of industrial systems, critical infrastructure, and scientific applications.
How DFOS Works
DFOS technology leverages the intrinsic scattering properties of light in optical fibers. By launching laser pulses into the fiber, a portion of the light is scattered back due to its interaction with the glass structure. The backscattered light is analyzed through its physical properties to extract valuable data regarding environmental conditions along the length of the fiber. Based on the chosen DFOS technology, this process enables the creation of a continuous spatial profile of temperature, strain, or acoustic activity over time.
Types of Scattering Used in DFOS
DFOS technology is based on different types of optical scattering phenomena:
- Raman Scattering: Used in Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) and Linear Heat Detecion (LHD) to measure accurate temperature variations along the fiber over time.
- Brillouin Scattering: Enables temperature measurements in Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS)
over long distances along an optical fiber.
In Distributed Temperature and Strain Sensing (DTSS) , it allows for the simultaneous and independent measurement of both temperature and mechanical strain. - Rayleigh Scattering: The foundation of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) , which captures vibrations and acoustic signals for security and structural monitoring.
Monitoring Capabilities of DFOS
DFOS systems enable high spatial resolution, real-time monitoring over extensive distances, offering valuable insights across various industries. Key capabilities include:
- Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) repurposes optical fibers into a dense network of acoustic sensors, capturing vibrations and acoustic signals in real time, benefiting security, transportation, and seismic monitoring applications.
- Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) utilizes fiber optic technology to deliver continuous temperature measurements along the entire fiber length, ensuring precise thermal profiling for industrial applications.
- Linear Heat Detection (LHD) uses fiber optic sensing cables to detect temperature changes along their length, providing fast, reliable and cost-effective fire and overheating detection for industrial, commercial, and critical infrastructure applications.
- Distributed Temperature & Strain Sensing (DTSS) extends the functionality of DTS by simultaneously detecting both temperature changes and mechanical strain, making it essential for structural integrity assessments and infrastructure monitoring.
Benefits & Advantages of Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing
- Continuous, Distributed Measurements: Provides a complete spatial profile rather than point-based data.
- High Sensitivity and Accuracy: Detects minor variations in temperature, strain, or acoustic signals.
- Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Ideal for deployment in harsh industrial environments.
- Cost-Effective & Low Maintenance: Glass fibers are durable and have long-term stability. Using existing fiber optic infrastructure reduces installation and maintenance costs.
- Scalability: Monitors assets over distances of up to 100 km or more without the need for additional sensors.
- Resistant to Harsh Environments: Fiber cables can operate in extreme temperatures, corrosive, or high-pressure environments.
AP Sensing's DAS System
DAS N51/N52-Series
Enhanced performance and measurement capabilities for protecting your valuable assets and infrastructure. Our fifth generation DAS features a world-leading measurement range for true phase-based systems without requiring additional amplification. It provides improved measurement performance with enhanced usability and reduced signal artifacts such as fading.
AP Sensing's DTS Systems
DTS N45-Series
AP Sensing covers all market requirements with its systems. Our DTS N45-Series is designed to operate anywhere – from the desert to the arctic. With the industry’s most complete set of certifications and stringent type tests, highest product quality and a long product life is guaranteed.
AP Sensing's LHD System
LHD N45-Series
With the third generation of our LHD system, the N45-Series, AP Sensing is raising the standard for fiber optic LHD. The N45-Series is certified to national and international standards for fire detection, offering the longest certified range on the market. No other fire detection system can withstand temperatures up to 750 °C (1400 °F) without losing monitoring capabilities.
With a proven track record and continued innovation, AP Sensing offers a completely integrated, end-to-end solution made in Germany. Our team works together with you to select the right combination of technologies to fit your requirements.
Key Takeaways
Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) technology is transforming the monitoring of industrial systems, critical infrastructure, and scientific applications—enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient operations.
DFOS leverages standard fiber optic cables to continuously measure temperature, strain, or acoustic signals along an entire asset. Advanced data processing algorithms interpret these signals to detect anomalies, structural changes, or environmental conditions, enabling early fault detection, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency. With its ability to cover vast distances, provide high spatial resolution, and deliver real-time insights, DFOS empowers operators to enhance safety, optimize performance, and respond proactively to potential issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This FAQ section shares practical, vendor-neutral insights to support engineers, operators, and decision-makers working with DFOS.
It is supported by Dr. Gregor Cedilnik, Principal Research Scientist at AP Sensing and a leading expert in distributed fiber optic sensing technologies. With decades of experience in fiber optics, photonics, and DFOS system design, he has authored numerous technical publications and patents and helped shape several of AP Sensing’s core platforms.
What is Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS)?
DFOS turns optical fibers into continuous sensors. A light pulse is launched into the fiber; tiny portions are scattered back along the route. By analyzing this backscatter, DFOS measures spatially resolved (distributed) temperature, strain, and acoustics/vibration along many kilometers of fiber, thus providing true gapless coverage of long assets.
How does DFOS work, in simple terms?
- A laser injects probe light pulses into an optical fiber.
- Microscopic scattering along the fiber (by physical effects known as Raman-, Brillouin- and Rayleigh scattering) returns tiny parts of it back to the instrument.
- The time of arrival reveals where the light was scattered (i.e. the distance along the fiber), the amount, phase and/or spectral shift of the backscatter depend on the temperature or strain and reveals what changed along the fiber.
Which DFOS technologies does AP Sensing offer?
- DAS - Distributed Acoustic Sensing (vibration/acoustics & event detection)
- DTS - Distributed Temperature Sensing (temperature profiles)
- LHD - Linear Heat Detection (code‑compliant fire / overheat detection)
- DTSS - Distributed Temperature & Strain Sensing (temperature and mechanical strain)
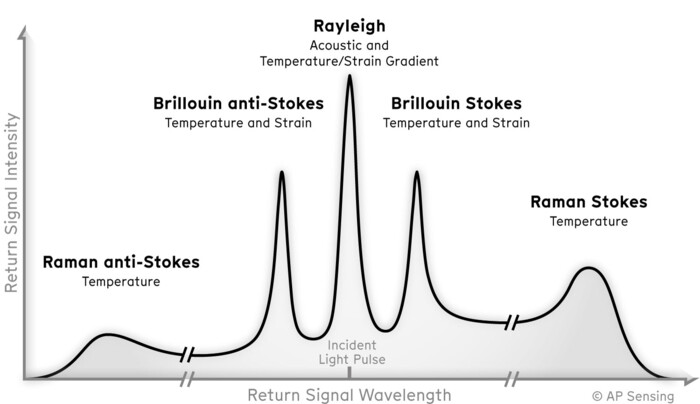
What is the difference between Raman, Brillouin, and Rayleigh backscatter in fiber optic sensing?
- Rayleigh - Sensitive to acoustics and vibration. It provides the strongest backscatter signal, enabling fast measurements with very high sensitivity over long distances. Used in DAS (Distributed Acoustic Sensing).
- Raman - Sensitive to temperature but unaffected by strain. Used in DTS (Distributed Temperature Sensing) and LHD (Linear Heat Detection).
- Brillouin - Sensitive to both temperature and strain. Offers a stronger signal than Raman, enabling very long-range measurements. Used in DTSS (Distributed Temperature & Strain Sensing).
Where is Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) used?
DFOS is widely used for monitoring and protection of critical assets across a range of industries. Key application areas include:
- Fire Detection: Transportation sector, production & storage facilities, energy sector, ships & vessels
- Power Grid Monitoring: HV cables (underground/subsea), overhead lines, substations, bus duct systems
- Process Automation & Pipeline Monitoring: Pipelines, LNG terminals, conveyor belts
- Critical Infrastructure Monitoring: Railways, underwater infrastructure, perimeters & borders
- Energy Exploration & Monitoring: Oil & gas upstream, carbon capture & storage, geothermal and geophysical
How far can a Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing (DFOS) system measure? What spatial resolution is typical?
Ranges and resolutions depend on modality and configuration:
- DAS - Condition-dependent reach (often >100 km) with meter resolution.
- DTS / LHD - multi‑kilometer coverage (tens of km) with meter to sub‑meter resolution
- DTSS (Brilloin) - very long reach (> 100km) for temperature & strain along large assets with meter resolution
Can I reuse existing telecom fibers for DFOS?
In many cases, yes, if factors like attenuation, routing, and fiber access are suitable. The project design should also take into account the fiber’s condition, the quality of splices and connectors, whether the fiber will be shared with live traffic, and the environmental ratings.
For harsh environments, high-temperature zones, or certified safety applications, using dedicated sensing fibers or ruggedized cables is often recommended.
How fast does the DFOS system detect anomalies?
- DAS – Detects events in milliseconds to seconds, offering near real-time response. Performance depends on the type and characteristics of the acoustic signals being monitored.
- DTS / LHD - Measurement times range from a few seconds to many minutes, depending on the averaging time and fiber length.
- DTSS – Measurement times can vary from sub-seconds to many minutes, depending on the project. This includes both long-term strain trends and faster dynamic events.
What influences DFOS measurement performance?
Measurement performance is affected by several factors, including the sensor length and fiber loss budget, the quality of splices/connectors, cable bending/ routing, instrument ambient temperature range, mechanical noise, instrument settings (like spatial resolution, pulse width, measurement time), and installation practices. To ensure reliable performance, early design reviews and commissioning tests are performed.